Mechanical Engineering :: Strength of Materials
-
The rectangular beam 'A' has length l, width b and depth d. Another beam 'B' has the same length and width but depth is double that of 'A'. The elastic strength of beam B will be __________ as compared to beam A.
-
When a closely-coiled helical spring is subjected to an axial load, it is said to be under
-
When a rectangular beam is loaded transversely, the zero stress is developed on the neutral axis.
-
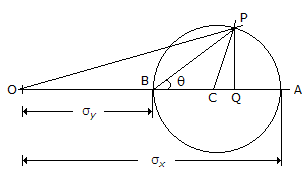
The given figure shows the Mohr's circle of stress for two unequal and like principal stresses (σx and σy) acting at a body across two mutually perpendicular planes. The normal stress on an oblique section making an angle θ with the minor principle plane is given by
-
According to Euler's column theory, the crippling load for a column of length (l) with one end fixed and the other end free is __________ the crippling load for a similar column hinged at both the ends.
-
If percentage reduction in area of a certain specimen made of material 'A' under tensile test is 60% and the percentage reduction in area of a specimen with same dimensions made of material 'B' is 40%, then
-
The shear force diagram for a simply supported beam carrying a uniformly distributed load of w per unit length, consists of
-
A body is subjected to two normal stresses 20 kN/m2 (tensile) and 10 kN/m2 (compressive) acting perpendicular to each other. The maximum shear stress is
-
When a cantilever beam is loaded at its free end, the maximum compressive stress shall develop at


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

