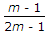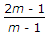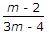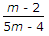Mechanical Engineering :: Strength of Materials
-
If the slenderness ratio for a column is 100, then it is said to be a __________ column.
-
A masonry dam may fail due to
-
In order to prevent crushing of masonry at the base of the dam, the maximum stress should be __________ the permissible stress of the soil.
-
When a body is subjected to two equal and opposite pushes, as a result of which the body tends to reduce its length, the stress and strain induced is compressive.
-
The bending moment at a point on a beam is the algebraic __________ of all the moments on either side of the point.
-
The maximum diameter of the hole that can be punched from a plate of maximum shear stress 1/4th of its maximum crushing stress of punch, is equal to (where t = Thickness of the plate)
-
Two closely coiled helical springs 'A' and 'B' are equal in all respects but the number of turns of spring 'A' is half that of spring 'B' The ratio of deflections in spring 'A' to spring 'B' is
-
The deformation per unit length is called
-
A thin cylindrical shell of diameter (d) and thickness (t) is subjected to an internal pressure (p). The ratio of longitudinal strain to volumetric strain is

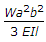 .
. 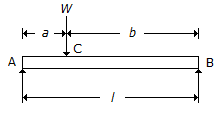

 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook