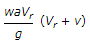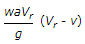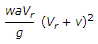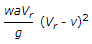Mechanical Engineering :: Hydraulic Machines
-
The speed of a turbine runner is
-
A ship with jet propulsion draws water through inlet orifices at right angles to the direction of its motion. The propelling force of the jet is (where a = Area of the jet, Vr = Relative velocity of the jet and ship = V + v, v = Velocity of the ship, and V = Velocity of the jet issuing from the ship)
-
Discharge of a centrifugal pump is (where N = Speed of the pump impeller)
-
In a reaction turbine, the draft tube is used
-
The power produced by the reaction turbine is __________ to the head of water.
-
Slip of a reciprocating pump is defined as the
-
The efficiency of a centrifugal pump will be maximum when the blades are bent backward.
-
Multi-stage centrifugal pumps are used to
-
The specific speed of a centrifugal pump, delivering 750 litres of water per second against a head of 15 metres at 725 r.p.m., is
-
Theoretical power required (in watts) to drive a reciprocating pump is (where w = Specific weight of liquid to be pumped in N/m3, Q = Discharge of the pump in m3/s, Hs = Suction head in metres, and Hd = Delivery head in metres)


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook