Mechanical Engineering :: Heat Transfer,Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
-
The process of heat transfer from one particle of the fluid to another by the actual movement of the fluid particles due to difference of density caused by temperature of the particle is known as
-
The thermostatic expansion valve is also called
-
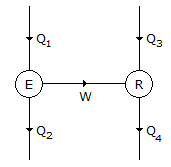
In figure shown, E is a heat engine with efficiency of 0.4 and R is a refrigerator. It is given that Q2 + Q4 = 3Q1. The C.O.P. of the refrigerator is
-
The specific humidity during cooling and dehumidification
-
The capillary tube, as an expansion device, is used in
-
In aircraft, air refrigeration Cycle is used because of
-
The material of pipe lines for a system using freon as a refrigerant should be
-
The temperature of air recorded by a thermometer, when the moisture present in it begins to condense, is called wet bulb temperature.
-
In a pressure enthalpy chart, the space to the left of the saturated liquid line represents


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

