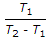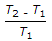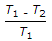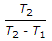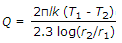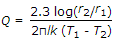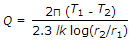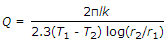Mechanical Engineering :: Heat Transfer,Refrigeration and Air Conditioning
-
The relative humidity lines on a psychrometric chart are
-
A vapour absorption refrigeration system
-
The rato of energy transferred by convection to that by conduction is called
-
A refrigerating system operating on reversed Brayton refrigeration cycle is used for maintaining 250 K. If the temperature at the end of constant pressure cooling is 300 K and rise in the temperature of air in the refrigerator is 50 K, then the net work of compression will be (assume air as working substance with cp = 1 kJ/kg)
-
A designer chooses the values of fluid flow rates and specific heats in such a manner that the heat capacities of the two fluids are equal. A hot fluid enters the counter flow heat exchanger at 100° C and leaves at 60° C. A cold fluid enters the heat exchanger at 40° C. The mean temperature difference between the two fluids is
-
The inclined and non-uniformly spaced straight lines on a psychrometric chart indicates wet bulb temperature.
-
The heat transfer by conduction through a thick cylinder(Q) is given by (where T1 = Higher temperature, T2 = Lower temperature, r1 = Inside radius, r2 = Outside radius, l = Length of cylinder, and k = Thermal conductivity)


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook