GATE 2017-2018 :: GATE Textile and Fibre
- A beaker contains 50 cc of an aqueous dye solution of concentration c (w/v). 25 cc of this solution is removed and replaced by 25 cc of distilled water. This process is repeated five more times. The final concentration of the solution is
- Assume that the rate of evaporation of moisture from a wet fabric during drying process is proportional to the amount of moisture present in the fabric. If 50 % of the moisture is evaporated in the first 5 minutes then the time (min) taken to evaporate 90 % of the moisture is approximately
- The number of neps in a carded web follows Poisson distribution with a mean of 100 per m2. The probability that there is no nep in an area of 645 cm2 is
-
A yarn of 24 mm length has a varying cross-section. The values of the cross-sectional area of yarn (mm2), measured at equal intervals of 4 mm from one end are 0.09, 0.12, 0.14, 0.15, 0.16, 0.13, 0.11The volume of yarn (mm3) estimated by using Simpson's 1/3 rule of numerical integration is
-
Match the property from Group I with the characterization technique from Group II.Group I Group IIP Spherulite size 1 Optical microscopyQ Degradation temperature 2 X-ray diffractionR Crystalline orientation 3 Differential scanning calorimetryS Melting temperature 4 Thermogravimetric analysis
-
Consider the following Assertion [a] and Reason [r] [a] In the case of manufactured fibre spinning, a circular spinneret orifice always results in circular cross-section of filaments in melt spinning, but the same is not true in dry spinning.[r] Melt spinning involves only heat transfer, whereas dry spinning involves heat as well as mass transfer.Determine the correctness or otherwise of the above Assertion [a] and Reason [r]
-
Consider the following assertion [a] and reason [r] in the context of the load-elongation curves of fibres F1, F2, and F3[a] Fibre F3 is the most suitable fibre for making a rope for mountaineering.
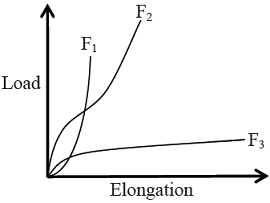 [r] Mountaineering rope should have high tenacity, high modulus and high work of rupture.Determine the correctness or otherwise of the above Assertion [a] and Reason [r]
[r] Mountaineering rope should have high tenacity, high modulus and high work of rupture.Determine the correctness or otherwise of the above Assertion [a] and Reason [r] - The winding speed (difference between bobbin speed and traveller speed) of yarn in a ring frame is 200 rev/min when bobbin diameter is 28 mm. If the bobbin diameter is increased to 35 mm, the winding speed (rev/min) would be
- The weight of material on a roving bobbin is 2.4 kg. The roving hank is 600 tex. If delivery rate is 20 m/min, the time (min) required to build the bobbin is
- The terry towel fabric is a


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

