GATE 2017-2018 :: GATE Civil
-
Elevation and temperature data for a place are tabulated below:
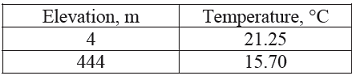 Based on the above data, lapse rate can be referred as:
Based on the above data, lapse rate can be referred as: - The percent voids in mineral aggregate (VMA) and percent air voids (Vv) in a compacted cylindrical bituminous mix specimen are 15 and 4.5 respectively. The percent voids filled with bitumen (VFB) for this specimen is:
-
Following bearings are observed while traversing with a compass.Line Fore Bearing Back BearingAB 126°45´ 308°00´BC 49°15´ 227°30´CD 340°30´ 161°45´DE 258°30´ 78°30´EA 212°30´ 31°45´After applying the correction due to local attraction, the corrected fore bearing of line BC will be:
- A theodolite is set up at station A and a 3 m long staff is held vertically at station B. The depression angle reading at 2.5 m marking on the staff is 6°10´. The horizontal distance between A and B is 2200 m. Height of instrument at station A is 1.1 m and R.L. of A is 880.88 m.Apply the curvature and refraction correction, and determine the R.L. of B (in m). __________
-
A propped cantilever made of a prismatic steel beam is subjected to a concentrated load P at mid span as shown.
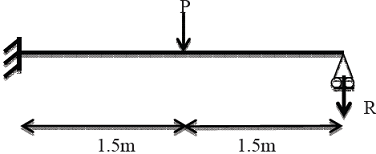 If load p = 80 kN,find the reaction R(in kN) (correct to 1-decimal place)using elastic analysis. __________
If load p = 80 kN,find the reaction R(in kN) (correct to 1-decimal place)using elastic analysis. __________ -
A propped cantilever made of a prismatic steel beam is subjected to a concentrated load P at mid span as shown.
 If the magnitude of load p is increased till collapse and the plastic moment carrying capacity of steel beam section is 90 kNm, determine reaction R(in kN) (correct to 1-decimal place) using plastic analysis. __________
If the magnitude of load p is increased till collapse and the plastic moment carrying capacity of steel beam section is 90 kNm, determine reaction R(in kN) (correct to 1-decimal place) using plastic analysis. __________ -
For a portion of national highway where a descending gradient of 1 in 25 meets with an ascending gradient of 1 in 20, a valley curve needs to be designed for a vehicle travelling at 90 kmph based on the following conditions. (i) headlight sight distance equal to the stopping sight distance (SSD) of a level terrain considering length of valley curve> SSD.(ii) comfort condition with allowable rate of change of centrifugal acceleration = 0.5 m/sec3.Assume total reaction time = 2.5 seconds; coefficient of longitudinal friction of the pavement= 0.35; height of head light of the vehicle =0.75 m; and beam angle = 1°.What is the length of valley curve (in m) based on the head light sight distance condition? __________
-
For a portion of national highway where a descending gradient of 1 in 25 meets with an ascending gradient of 1 in 20, a valley curve needs to be designed for a vehicle travelling at 90 kmph based on the following conditions. (i) headlight sight distance equal to the stopping sight distance (SSD) of a level terrain considering length of valley curve> SSD.(ii) comfort condition with allowable rate of change of centrifugal acceleration = 0.5 m/sec3.Assume total reaction time = 2.5 seconds; coefficient of longitudinal friction of the pavement= 0.35; height of head light of the vehicle =0.75 m; and beam angle = 1°.What is the length of valley curve (in m)based on the comfort condition? __________
-
At a station, Storm I of 5 hour duration with intensity 2 cm/h resulted in a runoff of 4 cm and Storm II of 8 hour duration resulted in a runoff of 8.4 cm. Assume that the Ï•-index is the same for both the storms. The Ï•-index (in cm/h) is:
-
At a station, Storm I of 5 hour duration with intensity 2 cm/h resulted in a runoff of 4 cm and Storm II of 8 hour duration resulted in a runoff of 8.4 cm. Assume that the Ï•-index is the same for both the storms.The intensity of storm II (in cm/h) is:


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

