EEE :: RL Circuits
-
A 1.5 k
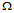 resistor and a coil with a 2.2 k
resistor and a coil with a 2.2 k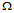 inductive reactance are in series across an 18 V ac source. The power factor is
inductive reactance are in series across an 18 V ac source. The power factor is -
The voltages in Problem 5 are measured at a certain frequency. To make the resistor voltage less than the inductor voltage, the frequency is
-
In a series RL circuit, 12 V rms is measured across the resistor, and 14 V rms is measured across the inductor. The peak value of the source voltage is
-
To increase the current in a series RL circuit, the frequency
-
A 470
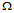 resistor and a coil with 125
resistor and a coil with 125 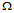 inductive reactance are in parallel. Both components are across a 15 V ac voltage source. Current through the inductor is
inductive reactance are in parallel. Both components are across a 15 V ac voltage source. Current through the inductor is -
A 1.2 k
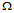 resistor is in series with a 15 mH coil across a 10 kHz ac source. The magnitude of the total impedance is
resistor is in series with a 15 mH coil across a 10 kHz ac source. The magnitude of the total impedance is -
When the frequency is decreased, the impedance of a parallel RL circuit
-
A 470
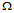 resistor and a 200 mH coil are in parallel. Both components are across a 1.5 kHz ac source. The total admittance of the circuit, in polar form, is
resistor and a 200 mH coil are in parallel. Both components are across a 1.5 kHz ac source. The total admittance of the circuit, in polar form, is -
A 12 k
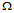 resistor is in series with a 90 mH coil across an 8 kHz ac source. Current flow in the circuit, expressed in polar form, is I = 0.3
resistor is in series with a 90 mH coil across an 8 kHz ac source. Current flow in the circuit, expressed in polar form, is I = 0.3 0° mA. The source voltage, expressed in polar form, is
0° mA. The source voltage, expressed in polar form, is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

