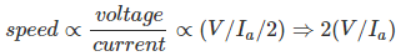EEE :: D.C. Motors
- Which D.C. motor will be preferred for machine tools?
- The speed of a D.C. series motor is
- The plugging gives the
- When two D.C. series motors are connected in parallel, the resultant speed is
- Which of the following motors one will choose to drive the rotary compressor?
- In case the back e.m.f. and the speed of a D.C. motor are doubled, the torque developed by the motor will
- Which of the following motors is usually used in household refrigerators?
- Which D.C. motor is preferred for elevators?
- During rheostatic braking of D.C. series motors
- In a D.C. generator all of the following could be the effects of iron losses except


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook