ECE :: Signals and Systems
-
A signal is sampled at Nyquist rate fs = 2f0. The function can be recovered from its samples only. If it is a
-
A voltage wave is v = 50 sin ωt. Its average value calculated over full one cycle is
-
If f1 (t) and f2 (f) are two functions of time and a and b are constants, then
-
A voltage wave is i = 100 sin (ωt). Its average value calculated over one half cycle is
-
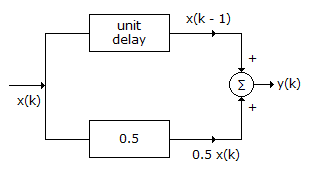
In the given figure 15.5 show a discrete time system consisting of a unit delay system, a multiplier and a summer, such that y(k) = x(k - 1) + 0.5 x(k). This system
-
An RLC series circuit has a variable inductance. The value of L for resonance conditions at fundamental frequency is 0.18 H. For resonance conditions at third harmonic frequency the value of inductance is
-
which of the following is not correct?
-
If function f(t) has an initial value f(0-) at t = 0-, the Laplace transform of
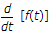 is
is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


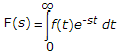
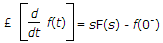
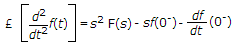
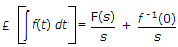
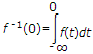
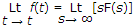
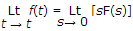
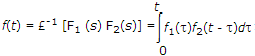
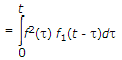
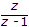
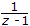
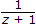
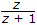
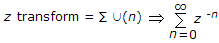
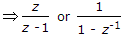 .
. .
.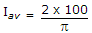 .
.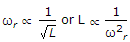 .
.