ECE :: Radio Receivers
-
The noise generated by a resistor depends upon
-
In a superheterodyne receiver
-
The function of an AM detector circuit is to
-
Which of the following should be used in order to prevent overloading or the last IF amplifier in a receiver?
-
Most popular IF for receivers tuning to 540 to 1650 kHz is
-
In a broadcast superheterodyne receiver
-
A duplexer is a device used to
-
A heterodyne frequency changer is called a
-
RF amplifiers are used in radio receivers for
-
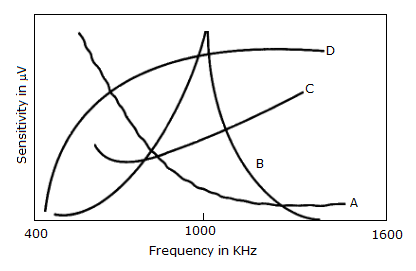
The sensitivity curve of a standard receiver is represented by


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

