ECE :: Materials and Components
-
A liquid has N permanent dipoles μp per unit volume and has been subjected to dc field for a long time such that orientation polarization is P0. At t = 0, the field is suddenly removed, then polarization
-
Assertion (A): Orbital magnetic moment of an electron in an atom is of the order of 1 Bohr magneton.
Reason (R): 1 Bohr magneton = 9.27 x 10-24 A/m2.
-
As per Bohr's postulate, only those circular orbits are stable for which the angular momentum is equal to an integer times
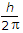 .
. -
Inductors used at V.H.F. are made using
-
If a capacitor C having selectivity factor Q is scaled down in all its dimensions by a factor K without any altering the dielectric material, the new capacitor will have capacitance and selectivity as
-
The hysteresis loss is
-
If m, v, r are the mass, velocity and radius of orbit of electron and h is Planck's constant, quantum condition for electron's orbit is
-
Assertion (A): For a magnetic material M = (μr - 1) H, where M is magnetic dipole moment/m3, H is field intensity A/m and μr is relative permeability.
Reason (R): μr can have any value from 0 to hundreds of thousands.
-
As regards ∈0 and ∈r (absolute and relative permittivity)






 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook



 , Q
, Q  .
. 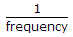



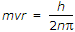
 .
.