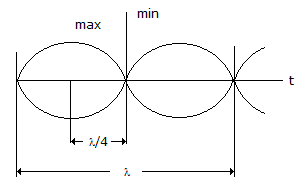ECE :: Electromagnetic Field Thoery
-
A 10 GHz signal propagates in a waveguide with a phase velocity of 4 x 108 m/s. If the signal produces standing wave in the guide, then the distance between successive minimal will be
-
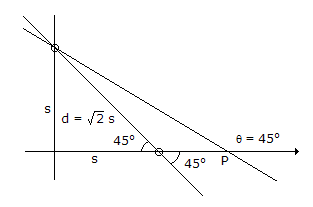
The incidence from dielectric medium 1 (ε1) into dielectric medium 2 (ε2), Brewster angle θB and the corresponding angle of transmission θt for
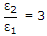 will be respectively
will be respectively -
A medium of relative permittivity εr2 = 2 forms an interface with free space. A point source of EM energy is located in the medium at a depth of 1 meter from the interface. Due to the total internal reflection, the transmitted beam has a circular cross-section over the interface. The area of the beam cross section at the interface is given by
-
A transmission line of characteristic impedance z0 = 50 Ω. Phase Velocity = 2 x 108 m/sec, and length l = 1 m is terminated by a load z1 = (30 - j 40) ohms. The input impedance of the line for a frequency of 100 MHz will be
-
A circular waveguide carries TE11 mode whose radial electric-field is given by
Er = E 0J1 (r) sin φ V/m
where 'r' is the radial distance in cm, from the waveguide axis. The cut-off wavelength of the mode is -
A uniform plane wave travelling in air is incident on the plane boundary between air and another dielectric medium with εr = 4. The reflection coefficient for the normal incidence is
-
A transmission line has characteristics impedance of (75 + j 0.01) Ω and is terminated in a load impedance of (70 + j 50) Ω. The transmission coefficient will be
-
Maximum effective aperture of an antenna which is operating at a wavelength of 3 meters and has a directivity of 100
-
A TV. transmitting aerial is fixed on top of a 150 metre tower located on a mountain 1200 m height. The range of transmitter is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


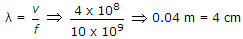
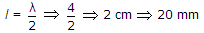 .
.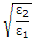
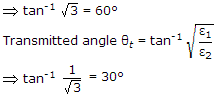
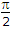 m2
m2 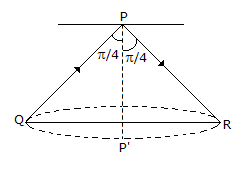
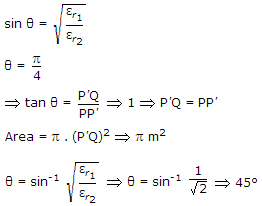
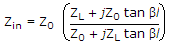 .
.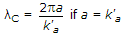 .
.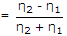
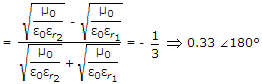 .
.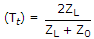 .
.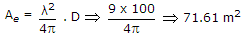 .
.