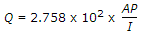Civil Engineering :: Water Supply Engineering
-
At the socket and spigot joint,
-
Gravity conduits for carrying water from the source are
-
Continuous flow of water can be expected from
-
A city supply includes
-
During treatment of water, sedimentation is done
-
Check valves are installed
-
The equation
 in which Q is yearly run off in cm, P is yearly total rainfall in cm, H is difference of R.L.s. of lowest and highest points and A is area of catchment in square metres, is known as
in which Q is yearly run off in cm, P is yearly total rainfall in cm, H is difference of R.L.s. of lowest and highest points and A is area of catchment in square metres, is known as -
If intensity of rainfall in cm per hour is I, percentage coefficient of run-off is P, area of catchment in square kilometres is A, the total run-off Q, is given by


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook