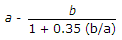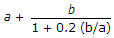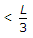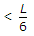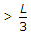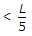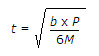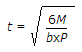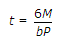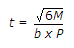Civil Engineering :: Steel Structure Design
-
Lug angle is
-
Effective length of a column effectively held in position and restrained in direction at both ends, is
-
A riveted joint many experience
-
If a pair of angles placed back to back in tension are connected by one leg of each angle, the net effective area of the section, is
-
IS : 800 - 1971 recommends that in a splice plate the number of rivets carrying calculated shear stress through a packing greater than 6 mm thick, is to be increased by 2.5% for every
-
To keep the intensity of bearing pressure between the column base and concrete, compressive throughout the length of the column base, the ratio of the moment M to axial load P should be
-
When the upper column does not provide full bearing area over lower column, the column splice is provided with the following assumption
-
For a steel member of slenderness ratio 350, the allowable stress is 76 kg/cm2 if it is
-
The permissible stress to which a structural member can be subjected to, is known as
-
If M is the moment due to a couple in a bearing plate whose width is b and allowable bending stress is P, the thickness (t) of the bending plate of the column splice, is


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook