Civil Engineering :: Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering
-
If e0, e, σ', σ0' have their usual meanings, the coefficient of compressibility (ac), is given by
-
A saturated soil sample has water content of 40% and specific gravity of soil particles 2.7. The void ratio of the soil, is
-
For testing a saturated clay for shear strength, the test recommended, is
-
The critical exist gradient of seepage water in soils, increases with
-
The coefficient ka of the active earth pressure, is given by
-
Pick up the correct statement from the following:
-
The shear strength of a soil
-
The property of a soil which permits water to percolate through it, is called
-
The triaxial apparatus is usually used for
|
A.
The void ratio in soils is defined as the ratio of the volume of voids to the volume of solids |
|
B.
The porosity of a soil is defined as the ratio of the volume of voids to the gross volume of the soil |
|
C.
The bulk density of a soil is defined as the unit weight of the soil |
|
D.
The dry density of a soil is defined as weight of solids to the total volume of the soil |
|
E.
All the above. |


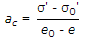
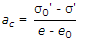

 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

