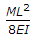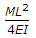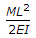Civil Engineering :: GATE Exam Questions
-
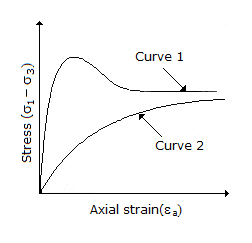
The stress-strain behaviour of soils as shown in the following figure corresponds to :
-
The maximum allowable compressive stress corresponding to lateral buckling in a discretely laterally supported symmetrical I beam does not depend upon :
-
The soils most susceptible to liquefaction are :
-
The following general statement may be made about the penetration value and softening point of bitumen
-
Sand drains are used to :
-
For a 'best' symmetrical trapezoidal section of an open channel with a given area of section and side slopes, one of the following statements holds true :
-
Temporary hardness in water is caused by the presence of
-
Bituminous materials are commonly use in highway construction because of their good
-
The stepped cantilever is subjected to moments, M as shown in the figure below. The vertical deflection at the free end (neglecting the self weight) is
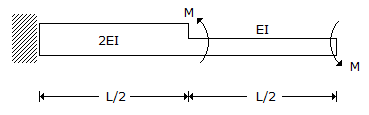
-
A road is provided with a horizontal circular curve having deflection angle of 55° and centre line radius of 250 m. A transition curve is to be provided at each end of the circular curve of such a length that the rate of gain of radial acceleration is 0.3 m/s3 at a speed of 50 km per hour. Length of the transition curve required at each of the ends is
|
A.
Curve 1 : Loose sand and normally consolidated clay
Curve 2 : Loose sand and over consolidated clay |
|
B.
Curve 1 : Dense sand and normally consolidated clay
Curve 2 : Loose sand and over consolidated clay |
|
C.
Curve 1: Dense sand and over consolidated clay
Curve 2: Loose sand and normally consolidated clay |
|
D.
Curve 1: Loose sand and over consolidated clay
Curve 2: Dense sand and normally consolidated clay |
|
A.
higher the penetration value, higher is the softening point
|
|
B.
higher the penetration value, lower is the softening point
|
|
C.
for very high and very low penetration value the softening point is very low
|
|
D.
absolutely no correlation can be drawn between penetration value and softening point of bitumen
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook