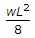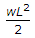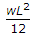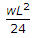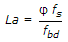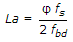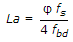Civil Engineering :: GATE Exam Questions
-
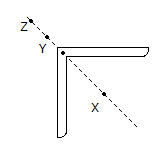
A point load of 700 kN is applied on the surface of thick layer of clay. Using Boussinesq's elastic analysis, the estimated vertical stress (σv) at a depth of 2 m and a radial distance of 1.0 m from the point of application of the load, is :
-
The liquid limit (LL), plastic limit (PL) and shrinkage limit (SL) of a cohesive soil satisfy the relation
-
A propped cantilever beam of span L, is loaded with uniformly distributed load of intensity w/unit length, all through the span. Bending moment at the fixed end is,
-
The sequent depth ratio of a hydraulic jump in a rectangular horizontal channel is 10.30. The Froude Number at the beginning of the jump is :
-
If φ = nominal diameter of reinforcing bar, fs = compressive stress in the bar and fbd= design bond stress of concrete, the anchorage length, La of straight bar in compression is equal to :
-
Alligator or map cracking is the common type of failure in
-
A steel beam supporting loads from the floor slab as well as from wall is termed as
-
For an anisotropic soil, permeabilities in x and y directions are kx and ky respectively in a two dimensional flow. The effective permeability keq for the soil is given by
-
Chemical oxygen Demand (COD) of a sample is always greater than Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD) since it represents :


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook