Civil Engineering :: GATE Exam Questions
-
The removal of dissolved organic matter occurs in
-
The toughness index of clayey soils is given by
-
A cantilever beam is shown in the below figure. The moment to be applied at free end for zero vertical deflection at that point is
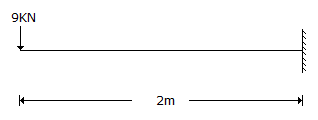
-
The order or the flexibility matrix for a structure is,
-
The Bowen ratio is defined as :
-
Water flows at a depth of 0.1 m with a velocity of 6 m/s in a rectangular channel. The alternate dpeth is
-
Two footings, one circular and the other square, are founded on the surface of a purely cohesionless soil. The diameter of the circular footing is same as that of the side of the square footing. The ratio of their ultimate bearing capcities is
-
An isochrone is a line on the basin map
-
Muskingum method for routing of flood
-
A frame ABCD is supported by a roller at A and is on a hinge at C as shown below
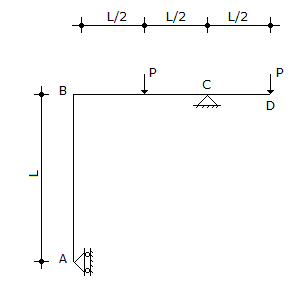
The reaction at the roller end A is given by
|
A.
Ratio of heat and vapour diffusivities.
|
|
B.
Proportionality constant between vapour heat flux and sensible heat flux.
|
|
C.
Ratio of actual evapotranspiration and potential evapotranspiration.
|
|
D.
Proportionality constant between heat energy used up in evaporation and the bulk radiation from a water body.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

