Civil Engineering :: Concrete Technology
-
Concrete containing
-
An ordinary Portland cement when tested for its fineness, should not leave any residue on I.S. seive No. 9, more than
-
The top diameter, bottom diameter and the height of a slump mould are :
-
Workability of concrete mix with low water cement ratio is determined by
-
While designing an air entrained concrete
-
Pick up the incorrect statemnt from the following. For performing compressive strength test of cement
-
For concreting tunnel linings, tran-portation of concrete is done by
-
The operation of removing humps and hollows of uniform concrete surface, is known as
-
The void ratio of
-
The type of aggregates not suitable for high strength concrete and for pavements subjected to tension, is
A.
|
|
B.
|
|
C.
|
|
D.
|
|
|
E.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


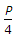 + 3.0 percentage of water where P is the percentage of water for standard consistency
+ 3.0 percentage of water where P is the percentage of water for standard consistency