Civil Engineering :: Applied Mechanics and Graphic Statics
- When a body of mass M1 is hanging freely and another of mass M2 lying on a smooth inclined plane(α) are connected by a light index tensile string passing over a smooth pulley, the acceleration of the body of mass M1, will be given by
- If two bodies of masses M1 and M2(M1 > M2) are connected by alight inextensible string passing over a smooth pulley, the tension in the string, will be given by
- The resultant of the forces acting on a body will be zero if the body
- For a body moving with simple harmonic motion, the number of cycles per second, is known as its
-
The beam shown in below figure is supported by a hinge at ‘A’ and a roller at ‘B’. The reaction RA of the hinged support ‘A’ of the beam, is
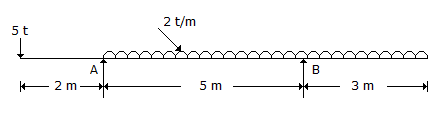
-
One end of an elastic string of natural length ‘l’ and modulus ‘X’ is kept fixed while to the other end is attached a particle of mass m which is hanging freely under gravity. The particle is pulled down vertically through a distance ‘x’, held at rest and then released.
The motion is -
A bullet weighing 10 gm moves with a velocity of l km/sec. Its kinetic energy is
(i) 5000 Nm
(ii) 5000 kg.m
(iii) 5000 J - The product of mass and velocity of a moving a body, is called
-
The C.G. of the shaded area of the below figure whose curve OM is a parabola from y-axis, is



 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

