Civil Engineering :: Applied Mechanics and Graphic Statics
- If the angle between the applied force and the direction of motion of a body, is between 90° and 180°, the work done, is called
- A particle of mass 2 kg executes simple harmonic motion of frequency 6/71 Hz and amplitude 0.25 m. Its maximum kinetic energy is
- A particle is dropped from a height of 3 m on a horizontal floor, which has a coefficient of restitution with the ball of 1/2. The height to which the ball will rebound after striking the floor is
- A glass ball is shot to hit a wall from a point on a smooth floor. If the ball returns back to the point of projection in twice the time taken in reaching the wall, the coefficient of restitution between the glass ball and the wall is
-
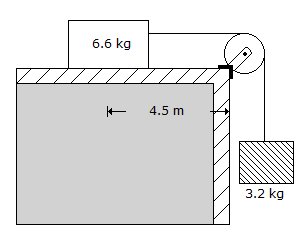
For the system of the loads shown in bellow figure, the time required for the 6.6 kg load to fall on the edge, is
- The moment of inertia of a triangular section (base b, height h) about centroidal axis parallel to the base, is
- The point about which combined motion of rotation and translation of a rigid body takes place, is known as
- Newton’s Law of Motion is:
|
A.
Everybody continues in its state of rest or of uniform motion in a straight line, unless it is acted upon by some external force |
|
B.
The rate of change of momentum is directly proportional to the impressed force, and takes place in the same direction, in which the force acts |
|
C.
To every action, there is always an equal and opposite reaction |
|
D.
All the above |


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

