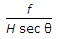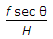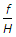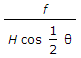Civil Engineering :: Advanced Surveying
-
Rotation of the camera at exposure about its vertical axis, is known as
-
The difference of height of two points whose parallax difference is 0.8 mm on a pair of stereo pair taken from a height H is 100 m. If mean photo base is 95.2 mm, the flying height is
-
The scale of a tilted photograph of focal length f, taken from an altitude H, along the plate parallel through plumb point, is
-
The flying height of the camera is 1, 000 m above mean ground level, the distance of the top of a Minar from a nadir point is 10 cm and the relief displacement of Minar is 7.2 mm. The height of the Minar, is
-
On vertical photographs, height displacement is
-
Assuming human normal vision distance 25 cm, smallest measurable angle 20", and introcular distance 6.5 cm, the smallest depth to be discerned is
-
The main object of the astronomer to obtain
-
If f is the focal length of the camera lens and θ is the angle of tilt, the distance of the plumb point from the principal point will be
-
Pick up the incorrect statement from the following. High oblique photographs


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook