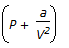Chemical Engineering :: Stoichiometry
-
Isotopes are atoms having the same
-
500 c.c. each of hydrogen at 700 mm Hg pressure and oxygen at 600 mm Hg pressure are put together in a vessel of 1 litre capacity. The final pressure of the gas mixture will be __________ mm Hg.
-
Which of the following terms of Vander Walls equation of state for a non-ideal gas accounts for intermolecular forces ?
-
What is the simplest formula of a compound containing 50% of element A (atomic weight = 10) and 50% of element B (atomic weight = 20) ?
-
The average value of heat of neutralisation of dilute solution of strong acids and strong bases is about __________ kcal/kg.mole of water formed.
-
In a mixture of benzene vapor and nitrogen gas at a total pressure of 900 mm Hg, if the absolute humidity of benzene is 0.2 kg benzene/kg nitrogen, the partial pressure of benzene in mm Hg is
-
For an ideal gas, the compressibility factor
-
In a neutral solution
-
In __________ process, ions of salts react with water to produce acidity or alkalinity.
-
Sodium __________ has inverted solubility curve i.e. its solubility increases with the lowering of temperature.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook