Chemical Engineering :: Process Control and Instrumentation
-
Thermal conductivity based continuous flue gas analyser makes use of varying thermal conductivity of the constituents of flue gases. Which of the following constituents of flue gases has the maximum thermal conductivity ?
-
Emf generated in a thermocouple depends on the temperature
-
Working principle of mercury in glass thermometer is based on the __________ of mercury with increase in temperature.
-
Radiation thermometer can not measure the temperature
-
Temperature measurement by optical pyrometer is done above __________ point, which is 1063°C.
-
Continuous flue gas analyser makes use of paramagnetic properties of some of its constituents, which move towards the strongest part of the magnetic field thus displacing diamagnetic gases. Which of the following gases is diamagnetic ?
-
Dilatometer is used to measure

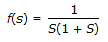 is
is
 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook


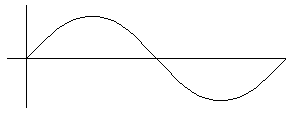
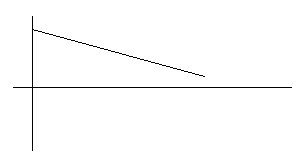
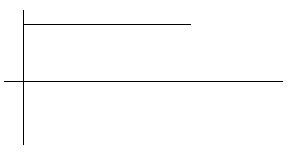
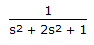 is
is