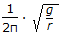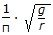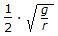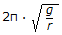Chemical Engineering :: Mechanical Operations
-
A screen is said to be blinded, when the
-
What is the critical rotation speed in revolutions per second, for a ball mill of 1.2 m diameter charged with 70 mm dia balls ?
-
Filter medium resistance is that offered by the
-
In a roll crusher, both the rolls
-
Tube mill compared to ball mill
-
Critical speed of rotation, N (in rps - rotation per second) of a trammel is equal to (where, g = acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/sec2 and, r = radius of trammel, metre. )
-
For the preliminary breaking of hard rock, we use a
-
Filtration operation carried out by continuous increase of the inlet pressure of slurry, is called the __________ filtration.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook