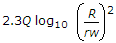Civil Engineering :: Water Supply Engineering
-
Asbestos pipes are
-
By boiling water, hardness can be removed if it is due to
-
Q is the discharge from an unconfined tube well with depression head s through its pipe of radius rw. If the radius of influence is R, the length of the required strainer, is
-
For determining the velocity of flow of underground water, the most commonly used non-empirical formula is
-
According to IS : 1172-1963, a minimum of 135 litres of water capita per day, is required for
-
The R.L. of ground water table on the sides of a valley is 1505 m whereas R.L. of the stream water is 1475 m. If 60° slope consists of pervious soil between R.L. 1485 m to 1500 m, the gravity spring may be expected at the point of reduced level
-
The factor affecting per capita demand, is
-
Pick up the incorrect statement from the following. The underground sources of water, is from


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook