Chemical Engineering :: Process Control and Instrumentation
-
The temperature range for which copper resistance thermometer can be used is __________ °C
-
Paramagnetism method is not used for the composition determination of __________ in gases.
-
For increased speed of response of an expansion pressure spring thermometer, the thermometer bulb should have a
-
Pressure of 0.0001 absolute psi can be measured by __________ gauge.
-
Pirani gauge is used for the measurement of
-
The __________ of the fluid contained in the temperature sensing element (i.e., bulb) of filled system thermometers changes with change in temperature.
-
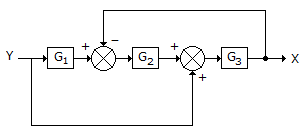
The characteristic equation for the control system with a closed loop transfer function G1/1 + G2 is given by 1 + G2 = 0. The characteristic equation for the control system
-
__________ thermometer can not measure sub-zero (< 0° C) temperature,


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook