Arithmetic Aptitude :: Area
FUNDAMENTAL CONCEPTS
1. Results on Triangle
-
Sum of the angles of a triangle is 180°.
-
The sum of any two sides of a triangle is greater than the third side.
-
Pythagoras Theorem:
In a right-angled triangle, (Hypotenuse)2 = (Base)2 + (Height)2.
-
The line joining the mid-point of a side of a triangle to the opposite vertex is called the median.
-
The point where the three medians of a triangle meet, is called centroid. The centroid divided each of the medians in the ratio 2 : 1.
-
In an isosceles triangle, the altitude from the vertex bisects the base.
-
The median of a triangle divides it into two triangles of the same area.
-
The area of the triangle formed by joining the mid-points of the sides of a given triangle is one-fourth of the area of the given triangle.
-
Results on Quadrilaterals:
-
The diagonals of a parallelogram bisect each other.
-
Each diagonal of a parallelogram divides it into triangles of the same area.
-
The diagonals of a rectangle are equal and bisect each other.
-
The diagonals of a square are equal and bisect each other at right angles.
-
The diagonals of a rhombus are unequal and bisect each other at right angles.
-
A parallelogram and a rectangle on the same base and between the same parallels are equal in area.
-
Of all the parallelogram of given sides, the parallelogram which is a rectangle has the greatest area.
-
IMPORTANT FORMULAE
-
1. Area of a rectangle = (Length x Breadth)
-
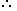 Length = \([\frac { Area } { Breadth } ]\)and Breadth =\([\frac { Area } { Length } ]\)
Length = \([\frac { Area } { Breadth } ]\)and Breadth =\([\frac { Area } { Length } ]\) -
2. Perimeter of a rectangle = 2(Length + Breadth).
-
Area of a square = (side)2 = \( \frac { 1 } { 2 } \)(diagonal)2.
-
Area of 4 walls of a room = 2 (Length + Breadth) x Height.
-
1. Area of a triangle = x \( \frac { 1 } { 2 } \)Base x Height.
2. Area of a triangle = s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
where a, b, c are the sides of the triangle and s = \( \frac { 1 } { 2 } \)(a + b + c). -
3 . Area of an equilateral triangle = \( \frac { \sqrt3} { 4 }\) x (side)2.
4. Radius of incircle of an equilateral triangle of side a =\( \frac { a} { 2 \sqrt3 }\)
5. Radius of circumcircle of an equilateral triangle of side a =\( \frac { a} { \sqrt3 }\)
6. Radius of incircle of a triangle of area
 and semi-perimeter r =
and semi-perimeter r = /s
/sVIII. 1.Area of parallelogram = (Base x Height).
2. Area of a rhombus =\( \frac { 1 } { 2 } \) x (Product of diagonals)
3 .Area of a trapezium = \( \frac { 1 } { 2 } \)x (sum of parallel sides) x distance between them
1. Area of a circle =
 R2, where R is the radius.
R2, where R is the radius.2. Circumference of a circle = 2
 R
R -
3. Length of an arc = \( \frac {2 \pi R} { 360 } \)where
 is the central angle.360
is the central angle.360 -
Circumference of a semi-circle =
 R.
R.
