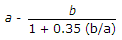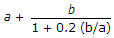Civil Engineering :: Steel Structure Design
-
Tacking rivets in compression plates not exposed to the weather, have a pitch not exceeding 300 mm or
-
Effective length of a column effectively held in position and restrained in direction at one end but neither held in position nor restrained in direction at the other end, is
-
For columns whose slenderness ratio is upto 160, the secant formula for the determination of allowable stress, is
-
The effective length of a double angle strut with angles placed back to back and connected to both the sides of a gusset plate, by not less than two rivets, is
-
According to the Unwin's formula, if t is thickness of the plate in cm, the nominal diameter of the rivet, is
-
A single angle in tension is connected by one leg only. If the areas of connecting and outstanding legs are respectively a and b, net effective area of the angle, is
-
The central deflection of a simply supported steel beam of length L with a concentrated load W at the centre, is
-
If L is the overall length of a combined footing having A as its area, d being the distance between the centre of gravity of the base and centre of the base, the larger width b is
-
On eccentrically loaded columns, the equivalent axial load may be obtained by
-
The distance between the outer faces of flanges of a plate girder, is known as
|
A.
adding the axial load, eccentric load, the product of the bending moment due to eccentric load and the appropriate bending factor
|
|
B.
adding the axial load and eccentric load and subtracting the product of bending moment and appropriate bending factor
|
|
C.
dividing the sum of axial load and eccentric load by the product of the bending moment and appropirate bending factor
|
|
D.
none of these.
|


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook