Chemical Engineering :: Mechanical Operations
-
General mechanism of size reduction in intermediate and fine grinder is by
-
A straight line is obtained on plotting reciprocal of filtration rate vs. the volume of filtrate for __________ flow of filtrate.
-
The work index in Bond's law for crushing of solids has the following dimensions
-
Ore concentration by jigging is based on the difference in the __________ of the particles.
-
Size measurement of ultrafine particles can be best expressed in terms of
-
Reduction ratio of crushers is the
-
Which is a secondary crusher for a hard & tough stone ?
-
Which of the following equations is Rittinger's crushing law ? (where P = power required by the machine, m = feed rate, k = a constant
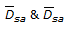 = volume surface mean diameter of feed & product respectively.)
= volume surface mean diameter of feed & product respectively.)


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook



