Chemical Engineering :: Mass Transfer
-
The falling rate period in the drying of a solid is characterised by
-
In which of the following unit operations, the selectivity is an important parameter ?
-
Which of the following is an undesirable characteristic for the solvent used in gas absorption ?
-
Which of the following equipments is not used for liquid dispersion ?
-
Diameter of raschig rings used in packed tower in industry is normally around __________ inches.
-
The diffusion co-efficient in m2 /s. of acetic acid in benzene (liquid in liquid) is
-
Pick out the wrong statement.
-
In case of non-ideal gases and liquids, the molal diffusivity
-
Condensation of a vapour-gas mixture just begins, when (where, p = partial pressure of the vapour P = vapour pressure of the liquid )
|
A.
The Reynolds analogy for mass transfer is given by Lewis relation and is applicable, when Schmidt number is one.
|
|
B.
Sherwood number for flow in pipes can be expressed as the ratio of the concentration gradient at wall to the overall concentration difference.
|
|
C.
According to film theory for equimolar counter diffusion, the mass transfer coefficient is given by DAB(b)P - 3, Q - 2
|
|
D.
The z-component of the total mass flux of a component A in binary mixture of A and B is given by - Dab'.dCA/dz.
|

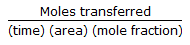

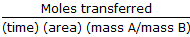

 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

