Chemical Engineering :: Heat Transfer
-
Heat transfer co-efficient (h) for a fluid flowing inside a clean pipe is given by
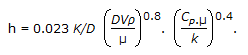 This is valid for the value of NRe equal to
This is valid for the value of NRe equal to -
Steam side heat transfer co-efficient in an evaporator is in the range of __________ kcal/hr.m2°C.
-
If h1 = inner film co-efficient and /h2 = outer film co-efficient, then the overall heat transfer co-efficient is
-
One kilogram of water at 0°C is changed to superheated steam of one atm pressure and 300° C. The major heat consumption in the process will be to
-
For __________ Prandtl number values, the heat conduction will be negligible in the buffer zone.
-
The radiation heat flux from a heating element at a temperature of 800°C, in a furnace maintained at 300°C is 8 kW/m2. The flux, when the element temperature is increased to 1000°C for the same furnace temperature is
-
Heat exchangers operating, when the asymptotic range is reached,
-
In case of a shell and tube heat exchanger, the minimum and maximum baffle spacing is respectively (where, D = inside diameter of the shell)
-
In case of heat transfer by conduction in a hollow cylinder, __________ mean area is used to calculate the heat transfer rate.


 Whatsapp
Whatsapp
 Facebook
Facebook

